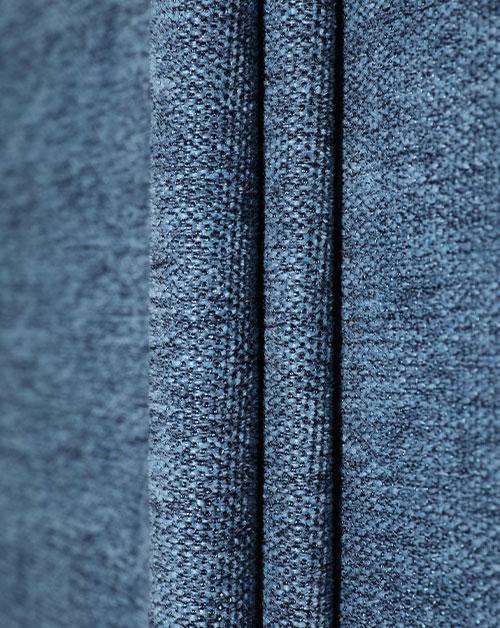
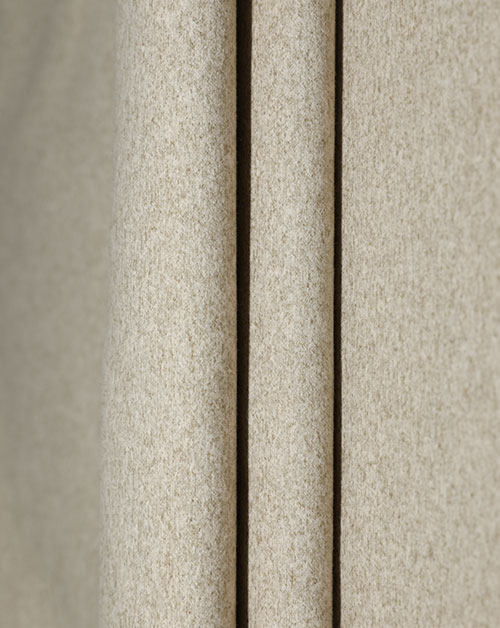
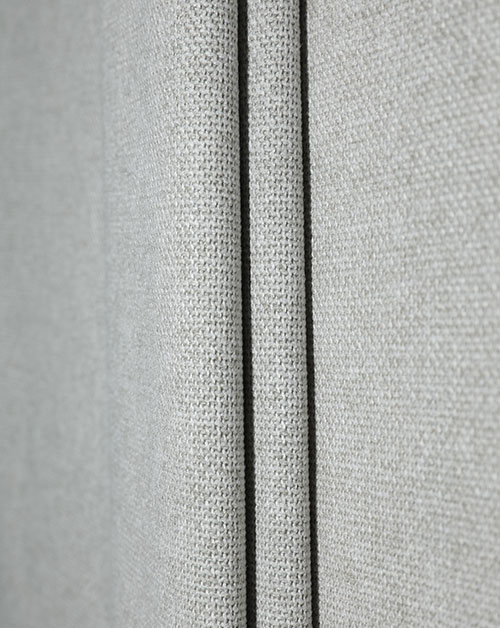
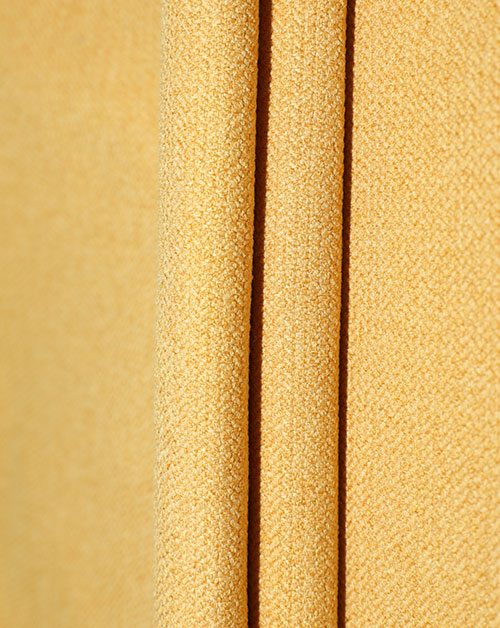
With the increasing global environmental awareness, the textile industry is undergoing an unprecedented green revolution. Among them, Recycled Fabric has become one of the most topical keywords with the most potential for industrial transformation. From discarded plastic bottles to recycling of old clothes, to the advent of high-performance functional fabrics, recycled fabrics are not only a material innovation, but also a manifestation of ecological responsibility. It is an important cornerstone of sustainable fashion and a key path to achieve the goal of "carbon neutrality".
What is recycled fabric? It is not just recycled materials
Recycled fabrics refer to fabrics that can be used for textiles that are re-produced through the recycling and reprocessing of waste resources. These waste resources come from a wide range of sources, including discarded PET beverage bottles, old clothes, scrapped fishing nets, industrial scraps, etc. Reprocessing these materials breaks the traditional production path of crude oil, cotton, etc. as raw materials, and reduces dependence on primary resources. Recycled polyester (rPET), recycled cotton, recycled nylon, etc. are all currently widely used types. These fabrics are gradually approaching primary materials in appearance, feel and performance, but behind them, energy consumption and carbon emissions are greatly reduced.

Full process analysis: the transformation from plastic bottles to high-performance fabrics
Take recycled polyester fabrics as an example. Its production process includes recycling and sorting, cleaning and crushing, melt spinning and post-processing. First, the recycled plastic bottles must be de-labeled and de-capped, then thoroughly cleaned by industrial washing equipment, and then crushed into fragments. After melt treatment, these fragments can be stretched into new polyester filaments or staple fibers through the spinning system, and then become finished fabrics through dyeing and weaving processes. Recycled cotton mainly breaks old clothes and textile scraps into fibers by mechanical means, and mixes a small amount of raw cotton to enhance the yarn strength, and then carries out the traditional spinning process.
What is the environmental value? Energy saving and carbon reduction are the hard truths
Compared with traditional fabrics, recycled fabrics have significant advantages in environmental benefits. The rPET production process can reduce carbon emissions by more than 30% compared to virgin polyester, while significantly saving water resources and energy. In the context of increasingly tight resources, it effectively alleviates the pressure on oil and arable land and reduces the problem of marine plastic pollution.

Full coverage of application scenarios: from fashion apparel to home building materials
The application of recycled fabrics is far from limited to the traditional clothing industry. In addition to the wide application in sportswear, casual wear, underwear, children's wear and other fields, more and more luggage and footwear brands have begun to introduce rPET or recycled nylon fabrics as the main material. Home textiles, such as sofa fabrics, curtains, bedding, etc., are also gradually realizing green substitution. In industrial fields such as construction, automobiles, and aviation, recycled fibers are also used in products such as sound-absorbing panels, composite materials, and automotive interiors, showing a multi-dimensional trend of "cross-border integration".
It can be said that recycled fabrics are not only an innovation of raw materials, but also a reshaping of the entire textile fashion ecological chain. Green is not just a trend, but the basic foundation of the brand's future. Recycled fabrics are redefining the true meaning of "face engineering" and will also become an important fulcrum for future industrial upgrading.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى